Abstract
This work presents global random walk approximations of solutions to one-dimensional Stefan-type moving-boundary problems. We are particularly interested in the case when the moving boundary is driven by an explicit representation of its speed. This situation is usually referred to in the literature as moving-boundary problem with kinetic condition. As a direct application, we propose a numerical scheme to forecast the penetration of small diffusants into a rubber-based material. To check the quality of our results, we compare the numerical results obtained by global random walks either using the analytical solution to selected benchmark cases or relying on finite element approximations with a priori known convergence rates. It turns out that the global random walk concept can be used to produce good quality approximations of the weak solutions to the target class of problems.
Authors
Nicolae Suciu
Tiberiu Popoviciu Institute of Numerical Analysis, Romanian Academy
Surendra Nepal
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Karlstad University, Universitetsgatan 2, Karlstad, 65188, Sweden
Yosief Wondmagegne
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Karlstad University, Universitetsgatan 2, Karlstad, 65188, Sweden
Magnus Ögren
School of Science and Technology, Örebro University SE-70182, Örebro, Sweden
HMU Research Center, Institute of Emerging Technologies, GR-71004, Heraklion, Greece
Adrian Muntean
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Karlstad University, Universitetsgatan 2, Karlstad, 65188, Sweden
Keywords
Global random walk approximation; Stefan-type moving-boundary problems; Finite element approximation, Order of convergence
Paper coordinates
N. Suciu, S. Nepal, Y. Wondmagegne, M. Ögren, A. Muntean, Global random walk for one-dimensional one-phase Stefan-type moving-boundary problems: Simulation results, Comp. Appl. Math., 44 (2025), art. no. 377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-025-03334-4
free available at the publisher: https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40314-025-03334-4.pdf
About this paper
Publisher Name
Springer
Print ISSN
2238-3603
Online ISSN
1807-0302
google scholar link
[1] S. C. Gupta, The Classical Stefan Problem: Basic Concepts, Modelling and Analysis, Elsevier 2003. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2017-0-02306-6
[2] J. Stefan, Über die Theorie der Eisbildung, insbesondere über die Eisbildung im Polarmeere, Ann. Physik Chemie 42 (1891), 269–286. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.18912780206
[3] D. A Tarzia and C. V. Turner, The one-phase supercooled Stefan problem with a convective boundary condition, Q. Appl. Math. 55(1) (1997), 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1090/qam/1433750
[4] A. Visintin, Models of Phase Transition, Birkhäuser, 1996.
[5] K. Tsunoda, Derivation of Stefan problem from a one-dimensional exclusion process with speed change, Markov Process. Relat. 21 (2015), 263–273.
[6] S. Nepal, Y. Wondmagegne and A. Muntean, Analysis of a fully discrete approximation to a moving-boundary problem describing rubber exposed to diffusants, Appl. Math. Comput. 442 (2023), 127733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2022.127733
[7] S. Nepal, R. Meyer, N. H. Kröger, T. Aiki, A. Muntean, Y. Wondmagegne and U. Giese, A moving boundary approach of capturing diffusants penetration into rubber: FEM Approximation and comparison with laboratory measurements, KGK-Kaut. Gumi. Kunst. 5 (2021), 61–69.
[8] D. A. Tarzia, L. T. Villa, On the free boundary problem in the Wen-Langmuir shrinking core model for noncatalytic gas-solid reactions, Meccanica 24 (1989), 86–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01560134
[9] T. Aiki, A. Muntean, Existence and uniqueness of solutions to a matheatical model predicting service life of concrete structures, Advances in Mathematical Sciences and Applications 19(1) (2009), 109–129.
[10] J. D. Evans, J. R. King, The Stefan problem with nonlinear kinetic undercooling, Q. J. Mech. Appl. 56(1) (2003), 139–161. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmam/56.1.139
[11] S. Nepal, M. Ögren, Y. Wondmagegne and A. Muntean, Random walks and moving boundaries: Estimating the penetration of diffusants into dense rubbers, Probabilist. Eng. Mech. 74 (2023), 103546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.probengmech.2023.103546
[12] N. Suciu, D. Illiano, A. Prechtel and F.A. Radu, Global random walk solvers for fully coupled flow and transport in saturated/unsaturated porous media, Adv. Water Resour. 152 (2021), 103935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2021.103935
[13] N. Suciu, Diffusion in Random Fields. Applications to Transport in Groundwater, Birkhäuser, Cham, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15081-5
[14] N. Suciu and F.A. Radu, Global random walk solvers for reactive transport and biodegradation processes in heterogeneous porous media, Adv. Water Resour. 166 (2022), 104268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2022.104268
[15] J.C. Strikwerda, Finite Difference Schemes and Partial Differential Equations, SIAM, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1137/1.9780898717938
[16] N. Suciu, F.A. Radu and E. Cătinaş, Iterative schemes for coupled flow and transport in porous media – Convergence and truncation errors, Numer. Anal. Approx. Theory 53(1) (2024), 158–183. https://doi.org/10.33993/jnaat531-1429
[17] S. Kutluay, A.R. Bahadir and A. Özdeş, The numerical solution of one-phase classical Stefan problem, J. Comput. Appl. Math. 81(1) (1997), 135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0427(97)00034-4
[18] S. Savović and J. Caldwell, Finite difference solution of one-dimensional Stefan problem with periodic boundary conditions, Int. J. Heat. Mass Tran. 46(15) (2003), 2911–2916. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(03)00050-4
[19] M. Mori, A finite element method for solving the two phase Stefan problem in one space dimension, Publ. Res. I. Math. Sci. 13(3) (1977), 723–753. https://doi.org/10.2977/prims/1195189605
[20] M. Mori, Stability and convergence of a finite element method for solving the Stefan problem, Publ. Res. I. Math. Sci. 12(2) (1976), 539–563. https://doi.org/10.2977/prims/1195190728
[21] M.-C. Casabán, R. Company and L. Jódar, Numerical difference solution of moving boundary random Stefan problems, Math. Comput. Simulat. 205 (2023), 878–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2022.10.026
[22] M. Ögren, Stochastic solutions of Stefan problems with general time-dependent boundary conditions, in: A. Malyarenko, Y. Ni, M. Rančié, S. Silvestrov (Eds.), Stochastic Processes, Statistical Methods, and Engineering Mathematics. SPAS 2019, Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol. 408, Springer, Cham, 2022. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17820-7_29
[23] C.J. Roy, Review of code and solution verification procedures for computational simulation, J. Comput. Phys. 205 (2005), 131–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2004.10.036
[24] C.D.Alecsa, I. Boros, F. Frank, P. Knabner, M. Nechita, A. Prechtel, A. Rupp and N. Suciu, Numerical benchmark study for flow in heterogeneous aquifers, Adv. Water Resour. 138 (2020), 103558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2020.103558
[25] P. M. Lewis, Laboratory testing of rubber durability, Polom. Test. 1 (1980), 167–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9418(80)90002-1
[26] M.J. Hayes and G.S. Park, The diffusion of benzene in rubber. Part 1.—Low concentrations of benzene, T. Faraday Soc. 51 (1955), 1134–1142. https://doi.org/10.1039/TF9555101134
[27] A. V. Kaliyathan, A. V. Rane, S. Jackson and S. Thomas, Analysis of diffusion characteristics for aromatic solvents through carbon black filled natural rubber/butadiene rubber blends, Polym. Composite 42 (2021), 375–396. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25832
[28] K. Kumazaki and A. Muntean, Global weak solvability, continuous dependence on data, and large time growth of swelling moving interfaces, Interf. Free Bound. 22(1) (2020), 27–50. https://doi.org/10.4171/ifb/431
[29] S. Nepal, Y. Wondmagegne and A. Muntean, Error estimates for semi-discrete finite element approximations for a moving boundary problem capturing the penetration of diffusants into rubber, Int. J. Numer. Anal. Mod. 19 (2022), 101–125. https://global-sci.org/intro/article_detail/ijnam/20351.html
[30] P. J. Roache, Code verification by the method of manufactured solutions, J. Fluids Eng. 124(1) (2002), 4–10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1115/1.1436090
[31] C. Cuchiero, C. Reisinger and S. Rigger, Implicit and fully discrete approximation of the supercooled Stefan problem in the presence of blow-ups, SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 62(3) (2024), 1145–1170. https://doi.org/10.1137/22M1509722
[32] F. A. Radu, I. S. Pop and S. Attinger, Analysis of an Euler implicit-mixed finite element scheme for reactive solute transport in porous media, Numer. Meth. Part. D. E. 26(2) (2009), 320–344. https://doi.org/10.1002/num.20436
Paper (preprint) in HTML form
Global random walk for one-dimensional one-phase Stefan-type moving-boundary problems: simulation results
Abstract
This work presents global random walk approximations of solutions to one-dimensional Stefan-type moving-boundary problems. We are particularly interested in the case when the moving boundary is driven by an explicit representation of its speed. This situation is usually referred to in the literature as moving-boundary problem with kinetic condition. As a direct application, we propose a numerical scheme to forecast the penetration of small diffusants into a rubber-based material. To check the quality of our results, we compare the numerical results obtained by global random walks either using the analytical solution to selected benchmark cases or relying on finite element approximations with a priori known convergence rates. It turns out that the global random walk concept can be used to produce good quality approximations of the weak solutions to the target class of problems.
Received: 2 November 2024 / Revised: 2 November 2024 / Accepted: 3 July 2025 /
Published online: 25 July 2025
© The Author(s) 2025
Keywords Global random walk approximation • Stefan-type moving-boundary problems • Finite element approximation Order of convergence Diffusion in rubber
Mathematics Subject Classification 35R37 • 65M75 • 65M 60
1 Introduction
Models for the penetration of diffusants in rubbers (or in other hyperelastic materials) can under certain conditions be formulated as one-dimensional moving-boundary problems. They are somewhat similar to the classical one-phase Stefan problem describing the melting of ice blocks (see e.g., Gupta 2003; Stefan 1891; Tarzia and Turner 1997). Briefly speaking, for any pair of space and time variables ( ), the evolution of the observable , denoting
adrian.muntean@kau.se
1 Tiberiu Popoviciu Institute of Numerical Analysis, Romanian Academy, Fântânele Str. No. 57, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
2 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Karlstad University, Universitetsgatan 2, 65188 Karlstad, Sweden 3 School of Science and Technology, Örebro University, 70182 Örebro, Sweden
4 HMU Research Center, Institute of Emerging Technologies, 71004 Heraklion, Greece
the mass concentration of the chemical species of interest, is governed in our context by the diffusion equation
where is a constant diffusion coefficient. This evolution is posed in the space-time domain
where denotes the maximum depth where the concentration has reached into the material and is a given final time of the overall process. We refer to this location as penetration depth and observe that it is not known a priori. To fix ideas, we take a Dirichlet boundary condition at the left (fixed) boundary and the Stefan condition at the right (moving) boundary in the classical Stefan problem (Stefan 1891). The latter essentially relates the speed of the moving boundary to the flux of the transported quantity , i.e.
In this case, we are led to the classical Stefan condition-the proportionality constant can be identified precisely and leads to the interface balance law
where is here the corresponding concept of latent heat needed for a purely diffusive setting. At this point, it is relevant to note that the classical setting of the Stefan problem takes as boundary condition at the moving boundary the expression . Now, prescribing as well the initial position of the moving boundary and the initial concentration profile , the complete formulation of the model is able to describe a wide class of phase transitions scenarios of first-order type; see Gupta (2003).
Within the present framework, we shall consider different information linked to the evolution of the moving boundary, namely we take
Such a relation is usually referred in the literature as a kinetic condition; see e.g. Visintin (1996). The original interface condition posed by Stefan (1891) to go along with the balance in interface fluxes describes an equilibrium picture. The kinetic representation of the speed describes a non-equilibrium scenario. For instance, if we think of small diffusant particles penetrating rubbers (see Sect. 4), the mentioned kinetic condition takes the particular form,
where the term mimics the swelling behavior of the rubber. To fit well to physically motivated scenarios, the homogeneous Dirichlet boundary condition at the fixed boundary is replaced by a flux boundary condition (of Robin type). It is worth also noting that the classical one-phase Stefan problem (so the equilibrium picture) admits probabilistic interpretations (see, for instance, Tsunoda 2015 and related work)-this gives trust in the quality of the model. On the other hand, in spite that most kinetic formulations are well-posed in suitable function spaces, the one-phase Stefan-type problem with kinetic condition does not seem to have available any obvious probabilistic interpretation. We do not attempt here to unveil such
probabilistic interpretation valid for a non-equilibrium phase transition. Instead, we wish to see to which extent a probabilistic-type numerical method can be designed to suit such class of problems. This leads to the main question that we are addressing in this paper, namely
(Q) To which extent a global random walk approach is able to approximate the weak solution of one-phase Stefan-type problems with kinetic condition.
Looking at (Q), one may wonder from where such sudden interest raises, as in fact one currently knows very well how to approximate numerically (in a both rigorous and efficient manner) the weak solution to the underlying moving-boundary problem; see e.g. Nepal et al. (2023b) for details on how finite element approximations work in this case (and other established numerical methods work as well). Our motivation really stems from the fact that in the engineering application that we have in mind [see the problem description in Sect. 4 and compare as well (Nepal et al. 2021) for more background on its potential technologic relevance 1 ]-only a finite number of particles succeed in fact to penetrate the hyperelastic material and affect the length of its lifetime. This makes us wonder whether a random walktype approach could describe perhaps better the physical picture. Such an approach would potentially be able to give insights on how many ingressing particles are needed to damage the host material. In this preliminary study, we wish to address the issue numerically. We proceed in the same spirit as in our previous work (Nepal et al. 2023a), where the used algorithms did employ classical random walks, but now we wish to benefit of the global random walk (GRW) structure which seems to lead to much faster calculations. Recently, the use of GRW was very successful in a number of situations involving reactive transport posed in fixed porous media domains, see, for instance, Suciu et al. (2021) and references cited therein. We aim to extend the GRW approach to the case of moving one-dimensional domains.
This paper is organized in the following fashion: Sect. 2 provides a brief description of the GRW method as applied for a diffusion problem. In the first part of Sect. 3, we introduce the one-dimensional classical Stefan problem and its GRW approximation. Additionally, we compare the GRW simulation results with finite element simulation results (with known convergence properties), and finally, we estimate the order of convergence of the GRW scheme. We are mainly interested in approximating moving interfaces whose speed is in some way controlled via a kinetic condition. To this end, we present in the second part of Sect. 3, the GRW simulation results for the Stefan-type problem with kinetic condition, where we numerically determine the order of convergence. The main aim of this paper is to apply the GRW method to approximate correctly the solution to the moving boundary problem describing the penetration of diffusants into rubber, which is discussed in Sect. 4. Our conclusion on the obtained results and potential directions for future research are presented in Sect. 5.
2 GRW approximation of diffusion
The theory behind GRW is described in Suciu (2019) and references cited therein. Here we only briefly recall the main basic ingredients. Numerical approximations reported here
will be provided by a GRW algorithm, free of numerical diffusion, which approximates the transported quantities with the same precision as that of the finite difference scheme, while keeping the corpuscular description of the corresponding continuous fields (Suciu 2019, Sect. 3.3). The GRW scheme can be derived as a randomization of the forward-time central-space finite difference discretization of the diffusion equation,
where is the approximation of the continuous concentration field at the lattice sites and time points is the space-time domain of the problem, and and are the space and time steps, respectively. The finite difference approximation is represented through the distribution of random walkers on the regular lattice, . With this, the finite differences scheme becomes
where . Accordingly, each group of particles is distributed over the lattice sites as
where represents the number of particles staying at the initial lattice site is the number of particles moving to the left, and finally, is the number of particles moving to the right. If the particles move according to the random walk rule, then corresponds to the jump probability, while the quantities are binomially distributed random variables. For consistency with the finite differences scheme, their ensemble average, denoted by an overbar in the following expressions, must verify the relations
In the GRW approach, instead of generating trajectories for each particle, the solution is obtained by computing the binomial random variables . The latter are accurately approximated with the "reduced fluctuations algorithm" (Suciu 2019, Sect. 3.3.2.2) in which the numbers and are rounded to integers with the floor function, the fractional parts are summed up, and a new particle is assigned to the lattice site where the sum reaches the unity (Suciu and Radu 2022, Sect. 3.1.1).
One notices that the normalization to the unity of the random walk probabilities imposes the constraint , equivalent to . This is the von Neumann condition that ensures the stability and the convergence of the finite differences scheme considered here (Strikwerda 2004, Sect. 6.3). On the other side, the relations verified by the quantities imply the equivalence between the ensemble-averaged GRW and the finite differences approximations. Note that the GRW algorithm is self-averaging in the sense that the single realization solution approaches its ensemble average with the increase of the number of particles; see Suciu (2019, Sect. 3.3.2.3). For large enough , the GRW and finite differences approximations are therefore identical in the limit of the machine precision, which implies the expected convergence of the GRW scheme. See also a numerical demonstration of the self-averaging of the GRW scheme for a non-linear diffusion equation (Richards’ equation) in Suciu et al. (2024, Sect. 3.1).
All the GRW simulations presented in this article use the fixed number of random walkers . That is, in particular, the concentrations are represented by mole fractions. The
algorithms are implemented in MATLAB with a generic structure as follows: a main code, where the initial data and the boundary conditions are formulated for transported quantities approximated as , with ; MATLAB functions for the GRW solvers that are called in the main code, describing the evolution of the groups of particles ; auxiliary MATLAB functions, e.g., to plot the results or to compute analytical solutions and various source terms occurring in the equations. This formulation facilitates the comparison with other discretization schemes presented in this article. However, when we are interested in describing the evolution of small numbers of ingressing particles, the same codes can be used to solve for , without the need to convert the number of particles to approximations of the continuous field . (The GRW algorithms presented in this article are implemented in MATLAB and are openly available in the Git repository https://github.com/PMFlow/Stefan_type_Problems.)
3 Benchmarking the GRW method for handling moving interfaces
3.1 The case of the classical Stefan problem
A Stefan problem is a specific initial boundary value problem describing the heat distribution in a phase-changing medium. It usually needs to be solved in a time-changing space domain with moving boundary conditions. As the moving boundary is a function of time and it has to be determined as a part of the unknowns of the problem, the exact solution to freeand moving-boundary problems is rarely available. Therefore, various numerical methods have been developed to approximate the solution to the Stefan problem, for instance, finite difference method (Kutluay et al. 1997; Savović and Caldwell 2003), finite element method (Mori 1977, 1976), probabilistic approaches (Casabán et al. 2023; Ögren 2022). In this section, we examine the application of the GRW method for solving the classical Stefan problem. We begin with providing a brief overview of the problem and its parameters. We then present the GRW simulation results and compare them against both the analytical solution (see for instance, Gupta 2003; Stefan 1891) and the random walk (RW) approximation from Ögren (2022). Finally, we study the grid convergence behaviour in the GRW method.
3.1.1 Problem formulation
We start off this section by introducing the classical Stefan problem and briefly explain the model’s parameters. The classical Stefan problem describes the solidification and melting process of ice. Initially, the ice is solid, so there is no liquid phase. We consider the temperature to be zero at the solid phase. For the ice can start to melt and thus we can have a water phase, i.e. a liquid phase. Let denote the temperature distribution in the liquid phase at time and at the position . Let denote the position of the moving interface that separates the solid and liquid phases, while is defined in the region . The problem reads: Find the temperature profile and the position of the moving interface for such that the couple ( ) satisfies the following set of equations:
| (1) | |||
| (2) |
| (3) | |||
| (4) | |||
| (5) | |||
| (6) |
The parameter represents the thermal diffusivity of the liquid and is defined by
Here is the corresponding heat conductivity, is the density and is the specific heat capacity of the liquid phase. Set as the specific latent heat required to melt ice. Assuming that the densities in the liquid and solid phases are equal, the analytical solution to (1)-(6) is given by Stefan (1891)
and
where is a given constant and satisfies the following algebraic equation
with and . We refer the reader to Gupta (2003) and Stefan (1891) for detailed descriptions of the Stefan problem and to Ögren (2022) for a random walk method approximating the solution of this problem. In the following we solve problem (1)-(6) in dimensionless form, with and , for the final time .
3.1.2 GRW convergence study for a benchmark case
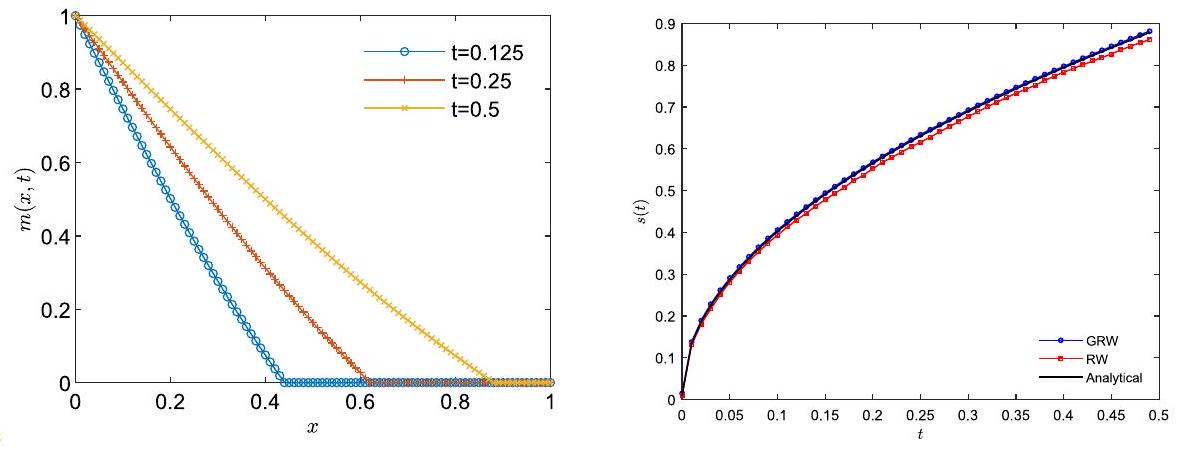
The Stefan problem described in Sect. 3.1.1 is solved now with a GRW scheme based on the algorithm described in Sect. 2 using the parameters of the numerical example presented in Ögren (2022).
The left-hand side of Fig. 1 shows the distribution of the water temperature at successive times, and in the right-hand side of Fig. 1 the GRW solution for the moving interface water/ice is compared with the exact analytical solution and the solution obtained with a random walk (RW) method presented in Ögren (2022, Fig. 8). The two numerical solutions were computed with the same spatial discretization . The relative errors of the RW and GRW solutions with respect to the analytical solution, computed in terms of vector norms, were of and , respectively.
Following the common approach of grid-convergence tests cf. e.g. Suciu et al. (2021), Suciu et al. (2024), Roy (2005) and Alecsa et al. (2020), we assess the convergence of the numerical solution ( ) to the analytical solution ( ) in terms of estimated orders of convergence ( ) given by the slope of the decay of the errors in the logarithmic scale after successively halving the discretization parameter , i.e.
| (7) |
| - | - | 0.04 | |||
| 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.05 | |||
| 0.92 | 1.02 | 0.08 | |||
| 1.00 | 1.03 | 0.32 | |||
| 1.11 | 1.03 | 1.84 |
where is the error measured in discrete norm (Alecsa et al. 2020) (i.e. in terms of , where is the Euclidean vector norm, in , for , and in [ ], for ). The tables presenting the convergence tests in the following have a generic structure: a column for the spatial discretization parameter , columns with errors of the profile and of the position of the moving boundary and the corresponding EOC, and another column with the computing times (CT) for successive .
The results of the convergence test and the corresponding computing times (CT) for the GRW approximation of the solution to the Stefan problem are presented in Table 1.
In the following, we compare the GRW approximation of the solution to the Stefan problem with approximations (of the same solution) obtained using the finite element method (FEM). To proceed with the FEM approach, we first transform the problem formulated in the moving domain ( ) into one posed for a fixed domain ( 0,1 ). To this end, we employ the Landau transformation . We then solve the transformed equations discretizing the fixed domain with a uniform grid size . We refer the reader to Nepal et al. (2021) for more details on how FEM works for one-dimensional moving-boundary problems.
The estimated orders of convergence and the corresponding computing times are presented in Table 2. Comparing with Table 1 we see that both GRW and FEM solutions converge with the same order . However, the GRW method, which solves the moving-boundary problem directly, without transformation to a fixed domain, approximates the solution with an accuracy that is systematically higher than that of the FEM solution and the corresponding computing times are one or two orders of magnitude smaller.
| - | - | 0.41 | |||
| 1.03 | 1.00 | 1.06 | |||
| 1.02 | 1.01 | 2.46 | |||
| 1.01 | 1.02 | 20.73 | |||
| 1.00 | 1.03 | 203.07 |
3.2 The case of the Stefan problem with kinetic condition
Now, we explore the convergence behaviour of GRW for the case of a Stefan problem with a kinetic condition. To begin with, we introduce a prototype model. Then, we construct an analytical solution which is further used in code verification and convergence tests.
3.2.1 Problem formulation
Consider that acts in the region . The problem reads: Find the profile and the position of the moving interface for such that the couple ( ) satisfies the following:
| (8) | |||
| (9) | |||
| (10) | |||
| (11) | |||
| (12) | |||
| (13) |
We notice that, unlike in the classical Stefan problem formulated in Sect.3.1.1, the interface condition (10) is now constrained by the kinetic condition (11) which also renders the coupled problem nonlinear.
3.2.2 Convergence study for a benchmark case
In the absence of analytical solutions, the code verification and the grid-convergence test can be done by computing errors with respect to manufactured solutions. The latter are functions of the dependent variables which have to fulfill the only requirement that the result of applying the differential operator , of the partial differential equation , is a nonvanishing function . Then, is an exact solution of the original partial differential equation with the source term added in the right-hand side, i.e., (Roache 2002).
In the following, we choose the analytical solution
| (14) |
| - | - | 0.33 | |||
| 1.48 | 1.00 | 1.12 | |||
| 1.49 | 1.00 | 7.13 | |||
| 1.49 | 1.00 | 44.91 | |||
| 1.50 | 1.00 | 376.95 |
Inserting (14) into the model (8)-(13) one obtains the source terms
in the right-hand sides of (8), (10), and (11), respectively. Also, the manufactured solution (14) fixes the boundary condition (9) to and verifies the initial conditions (12) and (13).
Preliminary tests with a linearization -scheme (Suciu et al. 2021) have shown that the nonlinearity arising when (11) is inserted in (10) is solved after the first iteration. Therefore, in solving Stefan problems with a kinetic condition we use the so-called explicit linearization of the moving boundary condition, consisting of replacing by in the right-hand side of (10). When, as in the present case, we evaluate the convergence with respect to an exact solution, the moving boundary condition (10) is also formulated exactly by using . (For details on the implementation see the code ’main_Stefan_kin_conv.m’ in the folder ’Stefan_kinetic’ of the Git repository.)
The results obtained with , and are presented in Table 3.
Observe that, when approximating , the convergence orders are improved compared to what is normally achieved for the classical Stefan problem.
4 GRW approximation capturing diffusion in rubber
Within this section we present GRW simulation results for a moving-boundary problem describing the penetration of diffusants into rubbers. Our interest in this particular scenario is linked with the many potential technological applications (cf. e.g. Nepal et al. 2021; Lewis 1980; Hayes and Park 1955; Kaliyathan et al. 2021), where we believe we can contribute with numerical predications of the durability (service life) of the rubber-based material.
We start by introducing and explaining the model equations. As a next step, we study the convergence behaviour for a benchmark case where we perform the grid-convergence test for a problem with the analytical solution. Finally, we present the GRW simulation results and compare them with the FEM and random walk (RW) solution for our model equations.
4.1 Problem formulation
We recall the following problem from Nepal et al. (2021): For a fixed observation time , the interval represents the duration of the involved physical processes. Let denote the time variable, the position of the moving-boundary at time and the space variable. The function represents the concentration of diffusant placed at position and time . The diffusants concentration acts in the region . The problem is: Find the diffusant concentration profile and the position of the moving-boundary such that the couple ( ) satisfies the following:
| (15) | |||
| (16) | |||
| (17) | |||
| (18) | |||
| (19) | |||
| (20) |
Here is the diffusion coefficient, is a kinetic coefficient, is a positive constant and is called the Henry constant. Additionally, is a function on describing the swelling of the rubber, represents the amount of diffusant concentration available at the boundary. We consider the diffusion equation in (15) to represent the role of diffusion for the evolution of the diffusant concentration . At the left boundary , we define the Robin-type boundary condition (16) to describe the inflow of diffusants into rubber. At the right boundary , we have the Robin boundary condition (17) that describes the mass conservation of the diffusants at the moving boundary. The ordinary differential equation (18) describes the speed of the moving boundary. In (20), denotes the initial position of the moving-boundary, while in (19) denotes the concentration of the diffusant at .
The model Eqs. (15)-(20) were designed to mimic experimental results involving the ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber being swollen in cyclohexane. We do not discuss here why this particular choice of materials is relevant and prefer instead to indicate a couple of mathematical results that delimitate the mathematical validity of the model. We refer the reader to Theorem 3.4 in Kumazaki and Muntean (2020) for detailed results on the global existence of weak solutions to (15)-(20) and continuous dependence with respect to initial data. The detailed description of model equations, laboratory experimental setup, and finite element simulation results is presented in Nepal et al. (2021). The finite element approximation recovered the experimental data well. To approximate the solution using the FEM, we first transform the moving domain ( ) into a fixed domain ( 0,1 ) by using the transformation . We then solve the transformed equations by discretizing the fixed domain with a uniform grid size . The convergence analysis of the finite element scheme is provided in Nepal et al. (2023b) and Nepal et al. (2022) where we achieved first-order convergence in both space and time for the position of the moving boundary and diffusant profile.
4.2 Convergence study for a benchmark case for diffusion in rubber
In the absence of analytical solutions, the code verification and the grid-convergence test can also here be done by computing errors with respect to manufactured solutions. From now onwards, we choose a linear dependence of on in (18). With this choice, (18) becomes
| (21) |
where is a constant parameter. This linear choice of is motivated by our previous work (Nepal et al. 2021, 2023a) where we explored the numerical simulation results for three different choices of and . We choose the following manufactured solution for the concentration profile and the diffusion front:
| (22) |
The exact solution (22) solves a modified problem, with the following source terms added in the right-hand side of (15)-(18):
While deriving the above source terms, we made use of the following properties of the manufactured solutions:
The initial conditions of the modified problem, corresponding to (19) and (20), are specified by the manufactured solution (22): .
We approach this problem (in dimensionless form) numerically via the GRW method. We make use of the following parameters: , and . The condition on the moving boundary is formulated exactly with the aid of the manufactured solution, as in Sect. 3.2.2. We compute the error of the concentration profile and moving front by comparing the GRW approximation with the manufactured solution in terms of the discrete norms introduced below Eq. (7). The obtained errors and estimated orders of convergence are shown in Table 4.
The performed grid-convergence tests indicate that the GRW approximations to the three Stefan-type problems converge with different rates: linear convergence for both concentration and penetration front in case of the classical Stefan problem (Table 1), convergence of about
| - | - | 0.05 | |||
| 2.13 | 1.99 | 0.06 | |||
| 2.03 | 1.99 | 0.07 | |||
| 2.02 | 2.00 | 0.18 | |||
| 2.01 | 2.00 | 0.81 |
| Parameters | Dimension | Typical values |
| Diffusion constant, | 0.01 ( ) | |
| Absorption rate, | 0.564 (mm/min) | |
| Constant, | ||
| Initial penetration front, | L | 0.01 (mm) |
| Initial diffusant concentration, | ||
| Concentration in lower surface of the rubber, | ||
| Henry’s constant, H | - | 2.50 (dimensionless) |
an order of 1.5 for concentration and linear convergence for the penetration front for the Stefan problem with kinetic condition (Table 3), and second-order convergence of both concentration and penetration front for the model of diffusion in rubbers (Table 4). Having in view the rigorous numerical analysis results behind the proofs of convergence rates of FEM approximations for this class of problems (cf e.g. Nepal et al. 2022, 2023b and references cited therein), we believe that the linear convergence for both concentration and penetration front observed in the case of the classical Stefan problem is what is in fact to be expected. The last two study cases indicate that, perhaps depending on the solution’s regularity and choice of parameters, some sort of super-convergence may take place. It would be interesting to investigate if one can delimitate rigorously parameter regimes and solution regularity classes where such super-convergence behavior can be guaranteed to happen.
4.3 A forecast exercise
After exploring the convergence of the GRW method for the problem with the manufactured solution in Sect. 4.2, our current goal is to validate the GRW method for (15)-(20). As the analytical solution is unavailable, we compare the GRW simulation results with the FEM approximation, the RW solution, and laboratory experimental data presented in Nepal et al. (2023a). The moving boundary condition in the GRW code is now formulated with the aid of the explicit linearization described in Sect. 3.2.2 above. (For details, see code ’main_RobinBC_conv.m’ in the folder ’Rubber’ of the Git repository.)
The typical values for the chosen parameters and their dimensions used in simulations are provided in Table 5, based on Nepal et al. (2023a).
The left-hand side of Fig. 2 shows the GRW simulation results compared to the RW and FEM solutions for the diffusant concentration profile. Similarly, the right-hand side of Fig. 2
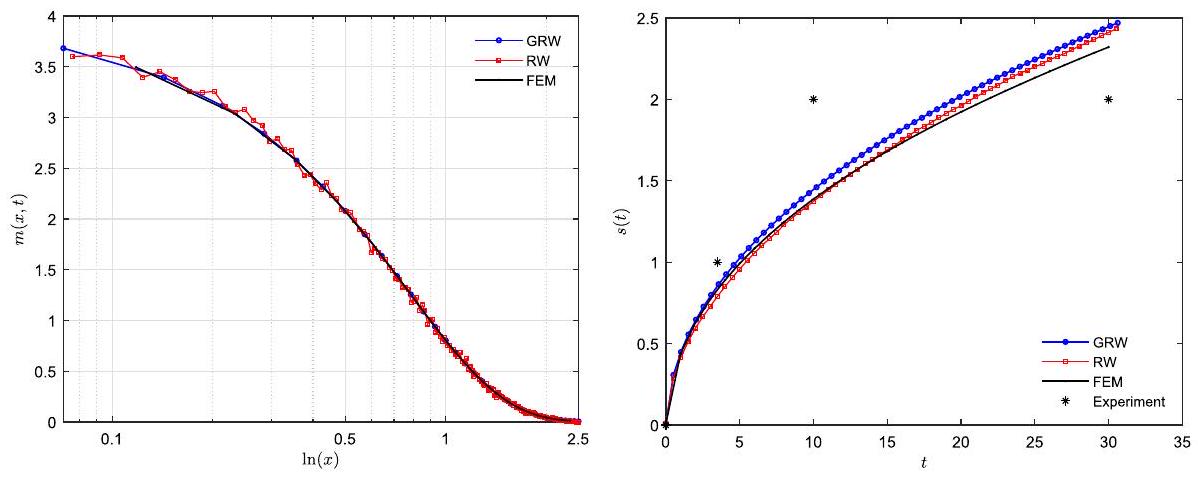
$. Right: Comparison of the position of the moving front approximated by GRW, RW, and FEM with laboratory experimental data}
compares the GRW solution with the RW and FEM solutions as well as with experimental data for the evolution of the penetration front. The GRW simulation results, for the concentration profile and the penetration fronts, are in good agreement with the RW and FEM results and are consistent with the laboratory experimental measurements of the penetration fronts.
While the RW concentration solution presented in Fig. 2, obtained with 500 random walkers in Nepal et al. (2023a), is affected by oscillations, the GRW solution using particles is smooth and practically coincides with the FEM solution. We also note that the second-order convergence of the GRW scheme for diffusion in rubbers (see Table 4) can only be obtained if the number of particles is at least (intuitively, for recovering much of the high-regularity of the solution).
Looking at Fig. 2, we notice that the numerically simulated penetration depths are within the expected physical range, i.e. they are closed to the measurement points. We refer the reader to Nepal et al. (2021) for the technical details of the experimental setup. Of course, one could perform a parameter identification procedure to identify the likelihood that our simulated moving boundary positions meet precisely the four measurements, but this is outside the scope of this work.
5 Conclusion
In this work, we presented the GRW approach approximating numerically one-dimensional moving boundary problems. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time when onedimensional moving-boundary problems are handled by means of the GRW methodology.
By means of numerical simulations, we propose a GRW approximation and perform a convergence study for the classical Stefan problem and for a Stefan-type problem with a kinetic condition, with direct application to a more practical scenario related to the penetration of diffusants into rubber-based materials. For all treated cases, both GRW and FEM approximations exhibited at least first-order of convergence for the position of the moving boundary and the concentration profile. This is consistent with the existing convergence proofs for the FEM approximation. However, in practice, improved convergence rates may be attained, as indicated in the present study by the numerically inferred EOC for solutions
of the Stefan-type problems with kinetic conditions. 2 This is often the case in numerical applications, see for instance (Radu et al. 2009).
Unlike the classical random walk method, the GRW method required less computing time than FEM. This makes one expect that, at least from the point of view of computing time, the GRW method is suitable for moving-boundary problems posed in higher-dimensional settings. Our work opens up new perspectives of the GRW approach which may be exploited in future works: (a) it has the same precision as that of the finite difference scheme, while keeping the corpuscular description of the corresponding continuous fields (as we said at the beginning of Sect. 2), (b) easy extension to two and three dimensions (Refs. Suciu et al. 2021, 2024), (c) appropriate for considering multicomponent reactions (Ref. Suciu and Radu 2022).
It remains an interesting and challenging task to prove rigorously uniform estimates on the indicated order of convergence. It is worth noting that remotely related work has been done very recently in Cuchiero et al. (2024) for the classical Stefan problem, the kinetic case remaining fully open.
Acknowledgements We thank U. Giese (Deutsches Institut für Kautschuktechnologie (DIK), Hannover, Germany) and N.H. Kröger (tesa SE, formerly with DIK) for posing us this problem. Fruitful discussions with K. Kumazaki (Kyoto, Japan) and T. Aiki (Tokyo, Japan) on the mathematical analysis of this moving-boundary problem are much appreciated. The work of S.N. and A.M. is partially funded by the Swedish Research Council’s project "Homogenization and dimension reduction of thin heterogeneous layers" with grant nr. VR 2018-03648. A.M. acknowledges also support from the Knowledge Foundation for the grants KK 2019-0213, KK 2020-0152, and KK 2023-0010.
Funding Open access funding provided by Karlstad University.
Data availability The codes used to produce our results are available upon request.
Declarations
Conflict of interest The authors have any financial or non-financial interests that are directly or indirectly related to this work.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
References
Aiki T, Muntean A (2009) Existence and uniqueness of solutions to a mathematical model predicting service life of concrete structures. Adv Math Sci Appl 19(1):109-129
Alecsa CD, Boros I, Frank F, Knabner P, Nechita M, Prechtel A, Rupp A, Suciu N (2020) Numerical benchmark study for flow in heterogeneous aquifers. Adv Water Resour 138:103558. https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.advwatres.2020.103558
Casabán M-C, Company R, Jódar L (2023) Numerical difference solution of moving boundary random Stefan problems. Math Comput Simulat 205:878-901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2022.10.026
Cuchiero C, Reisinger C, Rigger S (2024) Implicit and fully discrete approximation of the supercooled Stefan problem in the presence of blow-ups. SIAM J Numer Anal 62(3):1145-1170. https://doi.org/10.1137/ 22M1509722
Evans JD, King JR (2003) The Stefan problem with nonlinear kinetic undercooling. Q J Mech Appl 56(1):139161. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmam/56.1.139
Gupta SC (2003) The classical Stefan problem: basic concepts, modelling and analysis. Elsevier, London. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2017-0-02306-6
Hayes MJ, Park GS (1955) The diffusion of benzene in rubber. Part 1. Low concentrations of benzene. T Faraday Soc 51:1134-1142. https://doi.org/10.1039/TF9555101134
Kaliyathan AV, Rane AV, Jackson S, Thomas S (2021) Analysis of diffusion characteristics for aromatic solvents through carbon black filled natural rubber/butadiene rubber blends. Polym Compos 42:375-396. https:// doi.org/10.1002/pc. 25832
Kumazaki K, Muntean A (2020) Global weak solvability, continuous dependence on data, and large time growth of swelling moving interfaces. Interf Free Bound 22(1):27-50. https://doi.org/10.4171/ifb/431
Kutluay S, Bahadir AR, Özdeş A (1997) The numerical solution of one-phase classical Stefan problem. J Comput Appl Math 81(1):135-144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0427(97)00034-4
Lewis PM (1980) Laboratory testing of rubber durability. Polom Test 1:167-189. https://doi.org/10.1016/ 0142-9418(80)90002-1
Mori M (1976) Stability and convergence of a finite element method for solving the Stefan problem. Publ Res I Math Sci 12(2):539-563. https://doi.org/10.2977/prims/1195190728
Mori M (1977) A finite element method for solving the two phase Stefan problem in one space dimension. Publ Res I Math Sci 13(3):723-753. https://doi.org/10.2977/prims/1195189605
Nepal S, Meyer R, Kröger NH, Aiki T, Muntean A, Wondmagegne Y, Giese U (2021) A moving boundary approach of capturing diffusants penetration into rubber: FEM approximation and comparison with laboratory measurements. KGK-Kaut Gumi Kunst 5:61-69
Nepal S, Wondmagegne Y, Muntean A (2022) Error estimates for semi-discrete finite element approximations for a moving boundary problem capturing the penetration of diffusants into rubber. Int J Numer Anal Mod 19:101-125 (https://global-sci.org/intro/article_detail/ijnam/20351.html)
Nepal S, Ögren M, Wondmagegne Y, Muntean A (2023a) Random walks and moving boundaries: estimating the penetration of diffusants into dense rubbers. Probabilist Eng Mech 74:103546. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.probengmech.2023.103546
Nepal S, Wondmagegne Y, Muntean A (2023b) Analysis of a fully discrete approximation to a movingboundary problem describing rubber exposed to diffusants. Appl Math Comput 442:127733. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.amc.2022.127733
Ögren M (2022) Stochastic solutions of Stefan problems with general time-dependent boundary conditions. In: Malyarenko A, Ni Y, Rančié M, Silvestrov S (eds) Stochastic processes, statistical methods, and engineering mathematics. SPAS 2019, Springer proceedings in mathematics & statistics, vol 408. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17820-7_29
Radu FA, Pop IS, Attinger S (2009) Analysis of an Euler implicit-mixed finite element scheme for reactive solute transport in porous media. Numer Meth Part D E 26(2):320-344. https://doi.org/10.1002/num. 20436
Roache PJ (2002) Code verification by the method of manufactured solutions. J Fluids Eng 124(1):4-10. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1436090
Roy CJ (2005) Review of code and solution verification procedures for computational simulation. J Comput Phys 205:131-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2004.10.036
Savović S, Caldwell J (2003) Finite difference solution of one-dimensional Stefan problem with periodic boundary conditions. Int J Heat Mass Transf 46(15):2911-2916. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(03)00050-4
Stefan J (1891) Über die Theorie der Eisbildung, insbesondere über die Eisbildung im Polarmeere. Ann Physik Chemie 42:269-286. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp. 18912780206
Strikwerda JC (2004) Finite difference schemes and partial differential equations. SIAM, London. https://doi. org/10.1137/1.9780898717938
Suciu N (2019) Diffusion in random fields. Applications to transport in groundwater. Birkhäuser, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15081-5
Suciu N, Radu FA (2022) Global random walk solvers for reactive transport and biodegradation processes in heterogeneous porous media. Adv Water Resour 166:104268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2022. 104268
Suciu N, Illiano D, Prechtel A, Radu FA (2021) Global random walk solvers for fully coupled flow and transport in saturated/unsaturated porous media. Adv Water Resour 152:103935. https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.advwatres.2021.103935
Suciu N, Radu FA, Cătinaş E (2024) Iterative schemes for coupled flow and transport in porous mediaconvergence and truncation errors. Numer Anal Approx Theory 53(1):158-183. https://doi.org/10.33993/ jnaat531-1429
Tarzia DA, Turner CV (1997) The one-phase supercooled Stefan problem with a convective boundary condition. Q Appl Math 55(1):41-50. https://doi.org/10.1090/qam/1433750
Tarzia DA, Villa LT (1989) On the free boundary problem in the Wen-Langmuir shrinking core model for noncatalytic gas-solid reactions. Meccanica 24:86-92. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01560134
Tsunoda K (2015) Derivation of Stefan problem from a one-dimensional exclusion process with speed change. Markov Process Relat 21:263-273
Visintin A (1996) Models of phase transition. Birkhäuser, London
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
